I have cer file how generate key. The CSR will contain identifying information about the certificate requestor, and the public key.
Common OpenSSL Commands with Keys and Certificates
Mar 12, 2014 How to Generate RSA,DSA keys using OpenSSL. Openssl tutorial generate rsa,dsa keys learn how to verify rsa,dsa keys. May 22, 2019 How to Generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) With OpenSSL Step 1: Log Into Your Server. Open a terminal window. Step 2: Create an RSA Private Key and CSR. Step 3: Enter Your CSR Information. Your system should launch a text-based questionnaire. Step 4: Locate Certificate Signing Request. Openssl req -new-nodes-newkey rsa:2048 -keyout mydomain.key -out mydomain.csr This command will make a 2048-bit key, run the interactive prompt to populate the fields of the certificate signing request, and leave the private key unencrypted (-nodes). OpenSSL, however, currently defaults to creating 1024-bit keypairs. To create a 2048-bit private key and corresponding CSR (which you can send to a certificate authority to obtain your SSL certificate): openssl req -new -nodes -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout mydomain.key -out mydomain.csr. $ openssl req -new -key /path/to/wwwservercom.key -out /path/to/wwwservercom.csr This will fire up OpenSSL, instruct it to generate a certificate signing request, and let it know to use a key we are going to specify – the one we just created, in fact.
Generate RSA private key with certificate in a single command
Generate Certificate Signing Request (CSR) from private key with passphrase
Generate RSA private key (2048 bit)
Generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR)
Generate RSA private key (2048 bit) and a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) with a single command
Convert private key to PEM format
Generate a self-signed certificate that is valid for a year with sha256 hash
View details of a RSA private key
View details of a CSR
View details of a Certificate
View details of a Certificate in DER format
Rsa Key Generation
Convert a DER file (.crt .cer .der) to PEM
Convert a PEM file to DER
In this article you’ll find how to generate CSR (Certificate Signing Request) using OpenSSL from the Linux command line, without being prompted for values which go in the certificate’s subject field.
Below you’ll find two examples of creating CSR using OpenSSL.
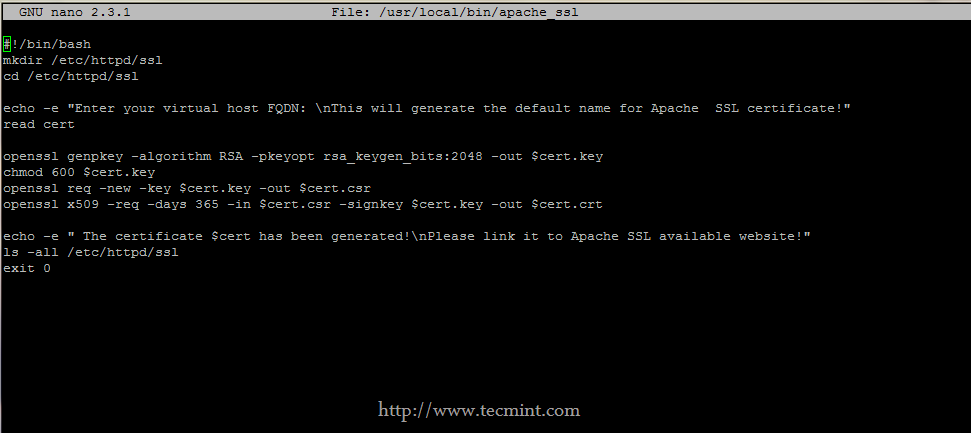
In the first example, i’ll show how to create both CSR and the new private key in one command.
I need to develop a solution to store both symmetric and asymmetric keys securely in AWS. These keys will be used by applications that are running on EC2s and Lambdas. 
And in the second example, you’ll find how to generate CSR from the existing key (if you already have the private key and want to keep it).
Both examples show how to create CSR using OpenSSL non-interactively (without being prompted for subject), so you can use them in any shell scripts.
Create CSR and Key Without Prompt using OpenSSL
Use the following command to create a new private key 2048 bits in size example.key and generate CSR example.csr from it:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| openssl req | certificate request generating utility |
| -nodes | if a private key is created it will not be encrypted |
| -newkey | creates a new certificate request and a new private key |
| rsa:2048 | generates an RSA key 2048 bits in size |
| -keyout | the filename to write the newly created private key to |
| -out | specifies the output filename |
| -subj | sets certificate subject |
Generate CSR From the Existing Key using OpenSSL
Use the following command to generate CSR example.csr from the private key example.key:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| openssl req | certificate request generating utility |
| -new | generates a new certificate request |
| -key | specifies the file to read the private key from |
| -out | specifies the output filename |
| -subj | sets certificate subject |
Automated Non-Interactive CSR Generation
The magic of CSR generation without being prompted for values which go in the certificate’s subject field, is in the -subj option.
| -subj arg | Replaces subject field of input request with specified data and outputs modified request. The arg must be formatted as /type0=value0/type1=value1/type2=…, characters may be escaped by (backslash), no spaces are skipped. |
Dsa Key
The fields, required in CSR are listed below:
Generate New Rsa Key Openssl Download
| Field | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| /C= | Country | GB |
| /ST= | State | London |
| /L= | Location | London |
| /O= | Organization | Global Security |
| /OU= | Organizational Unit | IT Department |
| /CN= | Common Name | example.com |
You’ve created encoded file with certificate signing request.
Openssl Generate Rsa Certificate
Now you can decode CSR to verify that it contains the correct information.